By Rolla Hassan, Ph.D
The 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report, published by IBM and the Ponemon Institute, reveals alarming trends in cybersecurity: the global average cost of a data breach has soared to $4.88 million, a 10% year-over-year increase and the sharpest spike since the pandemic. Drawing insights from 604 organizations across 17 industries and 16 countries, the report underscores the escalating financial, operational, and reputational risks of cyberattacks—and highlights how AI and automation are becoming indispensable tools for defense.
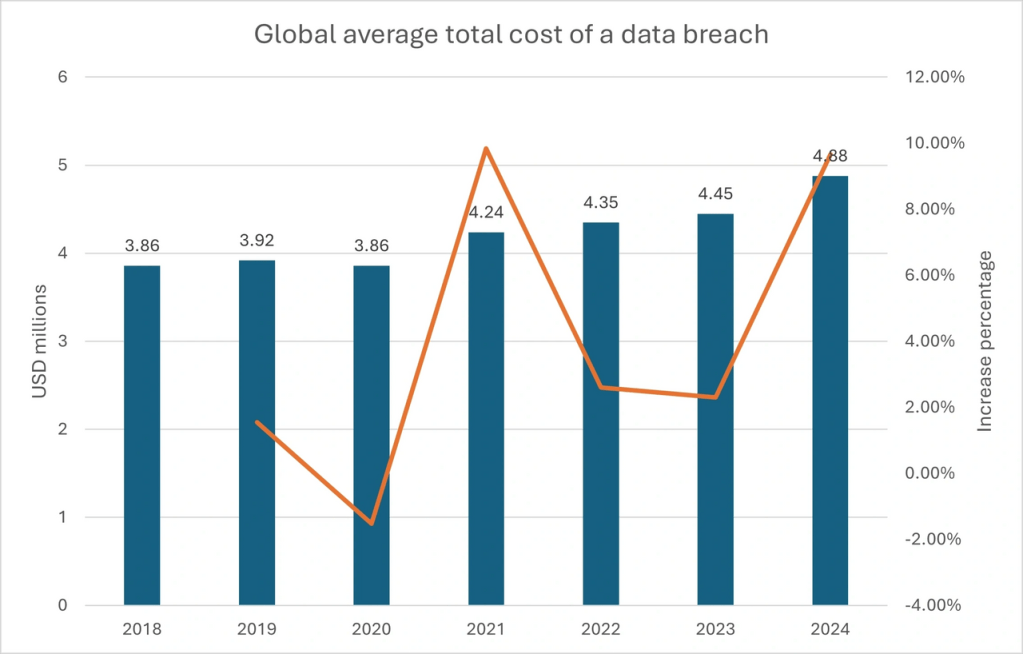
Analysis of the Global Average Total Cost of a Data Breach (2018–2024)
The graph illustrates the global average total cost of a data breach from 2018 to 2024, highlighting both monetary values (in USD millions) and year-over-year percentage changes. Below is a detailed analysis of the trends and implications:
- The cost of data breaches has risen significantly over the seven years, climbing from 3.86 million in 2018 to 4.88 million in 2024, a 26.4% cumulative increase.
- The most notable surge occurred in 2024, with costs jumping 10% year-over-year—the sharpest annual increase in the timeframe.
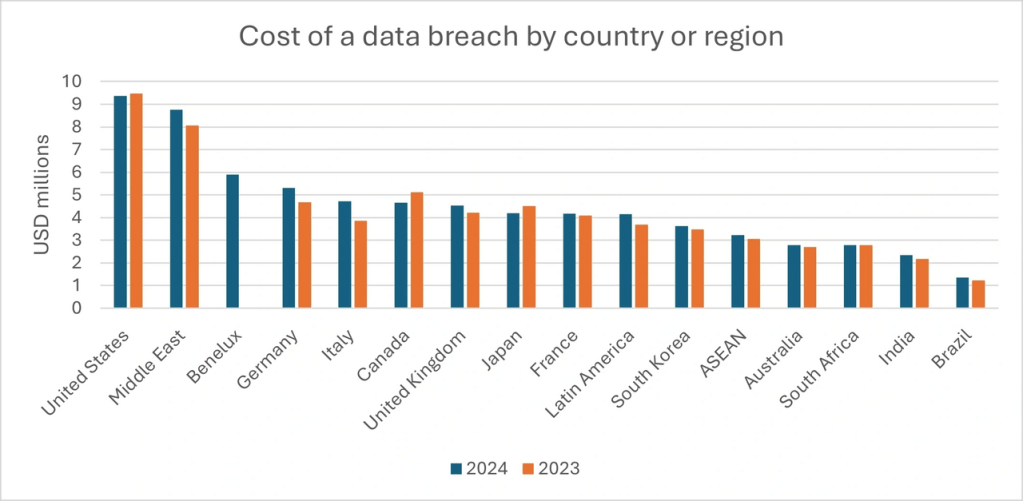
Analysis: Cost of a Data Breach by Country/Region (2023–2024)
The table below compares the average cost of a data breach across 16 countries/regions in 2023 and 2024 (in USD millions). Key trends, percentage changes, and insights are highlighted to contextualize the data.
- High Costs in Mature Markets: The U.S., Middle East, and Europe dominate the top due to high-value targets, stringent regulations, and advanced persistent threats.
- Rising Costs in Emerging Markets: Latin America (+12.7%), India (+7.8%), and Brazil (+11.5%) reflect rapid digitization outpacing cybersecurity readiness.
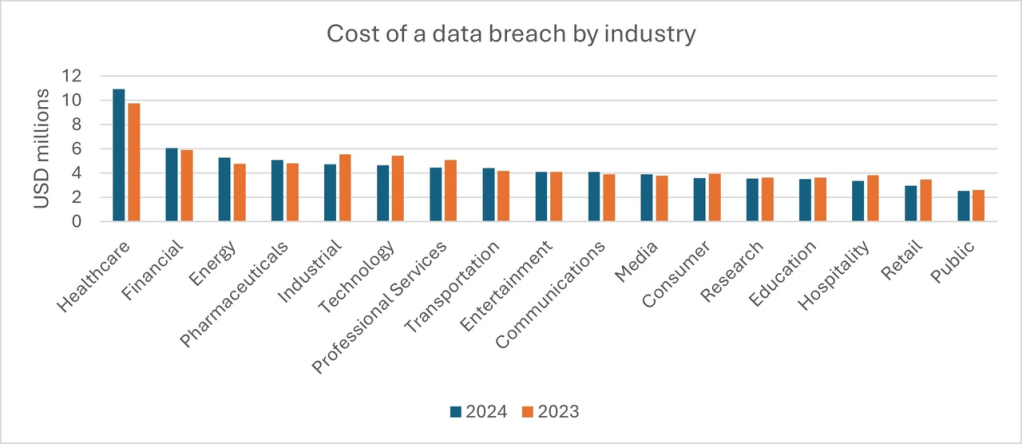
Analysis: Cost of a data breach by industry
This graph compares the average cost of data breaches across various industries for 2023 and 2024.
- Healthcare industry consistently has the highest cost of data breaches, increasing significantly from 2023 to 2024 (over 10 in 2024 compared to around 8 in 2023). This highlights the sensitive nature of data in this sector and the increased risks and regulatory requirements.
- Financial sector shows the second-highest costs, though the increase from 2023 to 2024 is less steep compared to healthcare. Financial data breaches can involve monetary theft and significant reputational harm.
Industries like Energy, Pharmaceuticals, Industrial, and Technology show similar breach costs in 2023 and 2024, with modest growth. These industries deal with intellectual property or critical infrastructure, making breaches costly but somewhat contained.
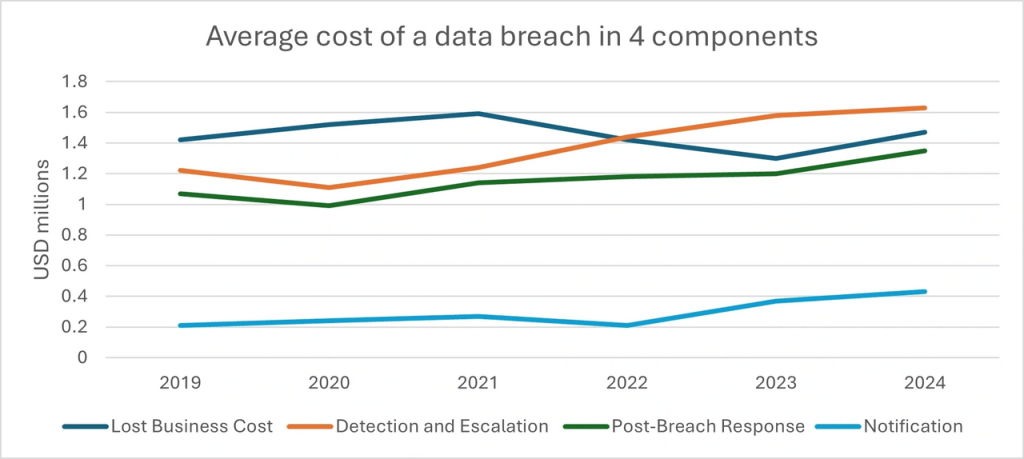
Analysis: Breakdown of Data Breach Costs (2019-2024)
The average cost of a data breach from 2019 to 2024 is divided into four key areas:
- Lost Business Cost
- Detection and Escalation
- Post-Breach Response
- Notification
Over the years, the costs in Detection and Escalation and Post-Breach Response have steadily increased, showing that breaches are becoming more complex and require more resources to manage. Additionally, Lost Business Costs have risen in 2024, emphasizing the difficulty of rebuilding customer trust and business stability after a breach.
1. Lost Business Cost
This includes the costs associated with losing customers and revenue during a breach. It covers:
- Loss of revenue due to system downtime
- The cost of losing and gaining customers
- Damage to the company’s reputation and goodwill
From 2019 to 2024, these costs increased from $1.42M to $1.63M.
2. Detection and Escalation
This covers the activities to detect and escalate the breach, including:
- Forensic and investigative work
- Assessments and audits
- Crisis management
- Communications to executives and boards
Detection costs have steadily grown, from $1.42M in 2019 to $1.63M in 2024. This increase reflects the growing complexity of breaches and the need for better tools and skilled teams.
3. Post-Breach Response
This involves activities to help affected individuals and comply with legal and regulatory actions, including:
- Help desks and communication channels
- Credit monitoring and identity protection services
- Issuing new accounts or credit cards
- Legal costs
- Offering discounts or compensation
- Regulatory fines
These costs have significantly increased from $1.22M in 2019 to $1.63M in 2024, driven by stricter regulations and higher customer expectations for post-breach support.
4. Notification
This involves notifying affected individuals, regulators, and other stakeholders, including:
- Sending emails, letters, or calls to individuals
- Determining regulatory requirements
- Communicating with regulators
- Hiring external experts
Notification costs have grown from $1.22M in 2019 to $1.63M in 2024, reflecting tougher regulatory demands and increasing customer expectations for transparency and support after a breach.
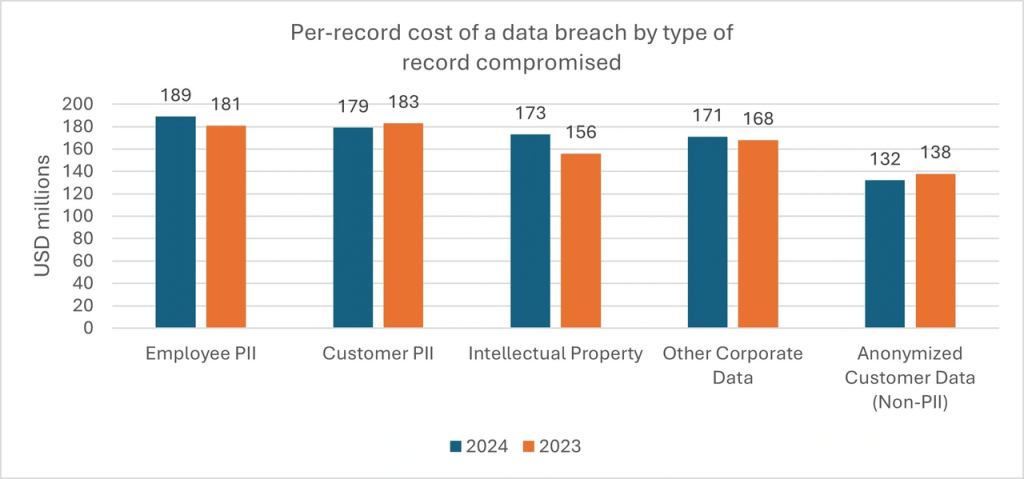
Per-record cost of a data breach by type of record compromised
The data is presented for two years, 2023 and 2024, in USD millions. Here’s a brief analysis based on the information:
- Employee PII (Personally Identifiable Information): This category likely represents the highest cost per record, indicating that breaches involving employee data are particularly costly. This could be due to the sensitive nature of the information and the potential for identity theft or fraud.
- Customer PII: Similar to Employee PII, breaches involving customer PII are also costly. This reflects the significant impact on customer trust and the potential regulatory fines associated with exposing customer data.
- Intellectual Property: Breaches involving intellectual property can be very damaging as they may lead to loss of competitive advantage and potential legal battles. The cost per record might be high due to the long-term financial implications.
- Other Corporate Data: This category might include less sensitive corporate information. The cost per record is likely lower compared to PII and intellectual property, but still significant due to potential operational disruptions.
- Anonymized Data: Anonymized data breaches might have the lowest cost per record since the data cannot be directly linked to individuals, reducing the risk of identity theft and regulatory penalties.
- Customer Data (Non-PII): This refers to customer data that does not include personally identifiable information. The cost per record is likely lower than PII but still notable due to potential impacts on customer relationships and business operations.
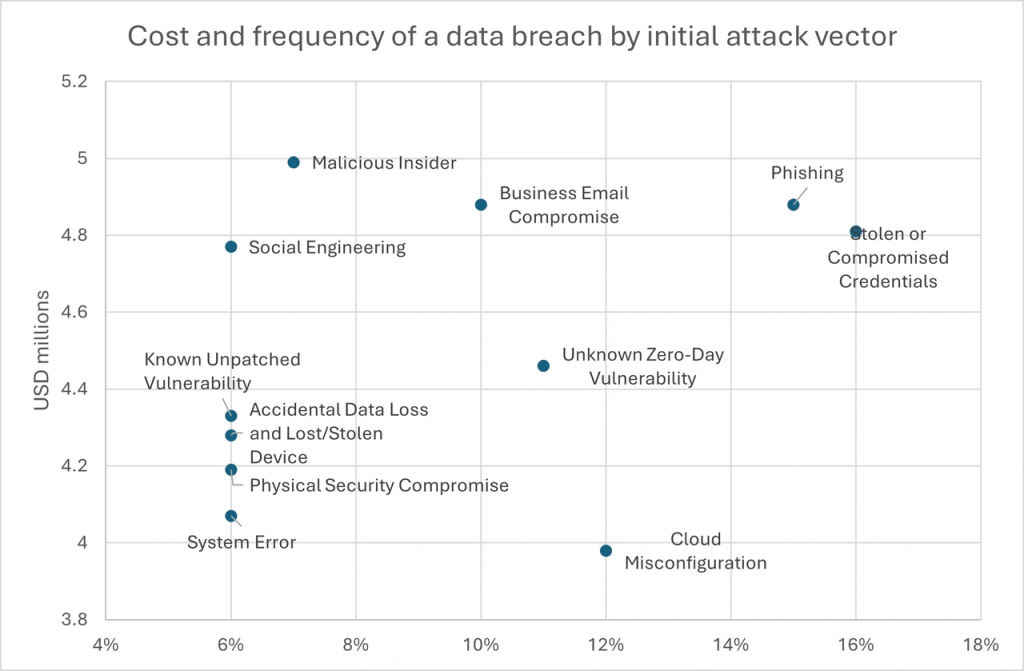
Cost and frequency of a data breach by initial attack vector
The figure below illustrates the frequency and cost of data breaches categorized by the initial attack vector. the frequency of attack vectors suggests that human-centric attacks (e.g., phishing, social engineering) and insider threats are likely to be the most costly due to their potential for widespread data exposure and reputational damage.
Conclusion
The 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report paints a stark picture of the escalating financial and operational toll of cyberattacks, with the global average cost of a data breach reaching a record high of $4.88 million. This 10% year-over-year increase underscores the growing sophistication of cyber threats and the challenges organizations face in defending against them. From human-centric attacks like phishing and social engineering to insider threats and zero-day vulnerabilities, the attack vectors are becoming more diverse and damaging.
Industries such as healthcare and finance continue to bear the brunt of these breaches due to the sensitive nature of their data and stringent regulatory requirements. Meanwhile, emerging markets are experiencing rapid cost increases as digitization outpaces cybersecurity readiness.
The breakdown of costs—ranging from lost business and detection efforts to post-breach response and notification—highlights the multifaceted impact of data breaches. As organizations grapple with these challenges, the adoption of AI-driven tools, automation, and zero-trust architectures is becoming essential to mitigate risks and reduce response times.
In an era where cyber threats are evolving faster than ever, investing in robust cybersecurity measures is no longer optional—it’s a business imperative. Organizations must prioritize employee training, advanced threat detection, and proactive defense strategies to safeguard their data, protect customer trust, and ensure long-term resilience in the face of an increasingly hostile digital landscape. The stakes have never been higher, and the time to act is now.
Data Reference:
IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024



Leave a comment