By: Abdelhak FODIL
Introduction
Industry 4.0 represents a paradigm shift characterized by hyper-connectivity, intelligent automation, and data analytics aimed at enhancing productivity, flexibility, and sustainability in manufacturing. Industrial 5G technology emerges as a pivotal force in realizing this vision, offering ultra-fast, reliable, and scalable communication solutions.
Overcoming Connectivity Barriers
Industrial 5G addresses the limitations of previous cellular technologies by providing download and upload speeds that can exceed 20 Gbps. This ultra-fast connectivity allows for the seamless connection of numerous devices—including machines, sensors, and robots—without congestion. This capability meets the growing data demands of complex industrial environments, fostering a more integrated and responsive manufacturing landscape (Wang & Gao, 2020).
Minimizing Latency
One of the standout features of 5G is its remarkably low latency, often reduced to mere milliseconds. This is crucial for real-time applications requiring immediate synchronization and responsiveness. Such advancements can significantly impact areas like high-precision robotic control, remote surgery, and autonomous vehicles, all of which rely on instantaneous data exchange and command execution.
Supporting Massive Simultaneous Connections
5G technology can support up to a million devices per square kilometer, making it indispensable for smart factories where thousands of machines and sensors need to communicate efficiently. This capability enables the real-time collection and analysis of vast data volumes, thus enhancing process optimization and intelligent decision-making.
Network Slicing for Tailored Solutions
Another innovative aspect of 5G is network slicing, which allows the creation of virtual networks tailored to the specific needs of different industrial applications. Critical applications, such as robotic control, can be allocated prioritized bandwidth and network resources even under high demand scenarios, ensuring consistent performance.
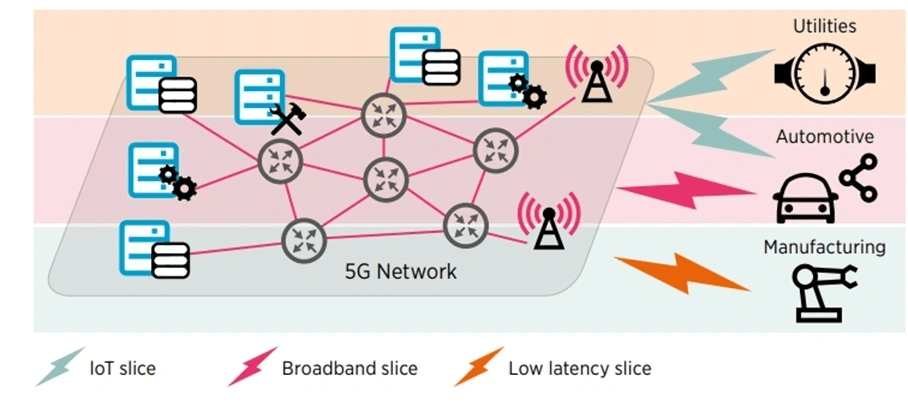
Figure 1: 5G networks subdivided into virtual networks each optimised for one business case (source GSMA)
Applications of 5G in Industry
According to Cheng et al. (2024), six primary applications of industrial 5G serve the broader goals of Industry 4.0, including Machine-to-Machine (M2M) communication, IoT manufacturing, cyber-physical systems (CPS), logistics and supply chain management, and digital twin-driven manufacturing.
M2M Communication
The rise of M2M communication is fundamental to smart manufacturing. This approach goes beyond simple data transmission; it establishes intelligent connections between machines and humans, facilitating:
- Information exchange between machines and systems.
- Transparent communication between machines and humans.
- Autonomous decision-making by machines based on shared data analytics.
M2M communication enhances operational efficiency through better collaboration between machines and human operators, optimizing manufacturing processes.
IoT Manufacturing
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) connects various devices, sensors, and information systems to create a comprehensive data ecosystem, contributing to the “Internet of Everything” (Khurpade et al., 2018). This connectivity strengthens ties between industry and users, improving customer experiences and after-sales services.
CPS Enhancement
Industrial 5G significantly benefits CPS by improving their performance and opening up new application possibilities:
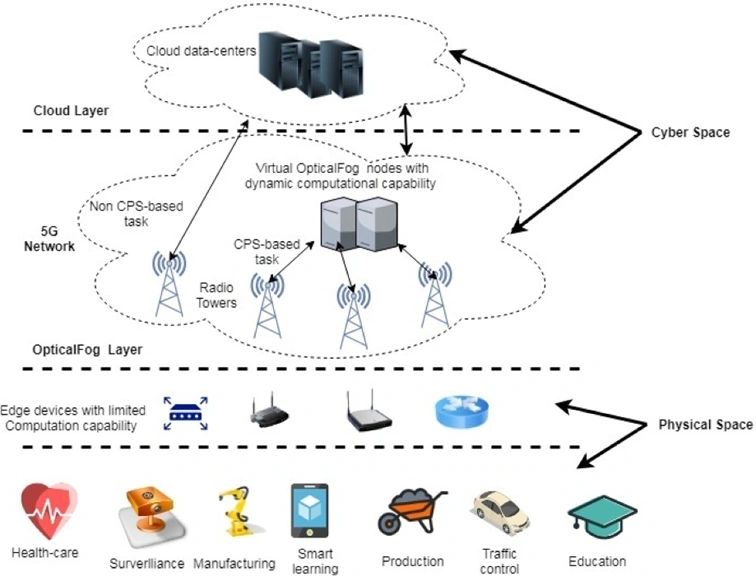
Figure 2 : The 5G brick within a CSP system (source IET)
- Ultra-low latency enhances real-time communication between physical and digital components.
- Increased reliability ensures continuous operation in challenging conditions.
- Support for mobility allows CPS to move freely without losing connectivity.
- The ability to handle massive connections secures seamless operations in complex environments.
- Enhanced security features protect data and systems from cyber threats.
Logistics and Supply Chain Transformation
The low latency, high throughput, and massive connection capabilities of 5G can revolutionize logistics and supply chain management by enabling:
- Real-time tracking of inventory and material flows through connected sensors and RFID tags.
- Automated management of autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs) with high precision and low latency.
- Predictive maintenance by analyzing real-time machine performance data to anticipate failures.
- Augmented reality applications to assist production operators with real-time instructions.
- Remote collaboration for problem-solving, connecting experts to on-site cameras and sensors.
Digital Twin-Driven Manufacturing
5G’s capabilities are crucial for digital twin technologies, which create dynamic virtual representations of physical objects or processes. By collecting real-time data, manufacturers can:
- Predict and prevent failures by simulating operational scenarios.
- Optimize production processes through modeling different configurations.
- Reduce costs by enhancing efficiency and minimizing waste.
- Improve product quality by identifying and addressing defect causes.
- Accelerate innovation by testing new products and processes before real-world deployment.
Figure 3: Digital twin concept (source Ericsson)
Conclusion
The advent of industrial 5G marks a transformative era for global manufacturing, unlocking vast potential for optimizing processes, increasing flexibility, and driving innovative products and services. However, significant challenges remain in its widespread adoption, including technology maturity, deployment costs, integration complexities, security, data privacy concerns, and skills shortages.
A collaborative approach among all ecosystem players is essential to overcome these hurdles and ensure that industries worldwide harness the full potential of industrial 5G. By actively engaging in this transformation, countries can position themselves as leaders in this critical technological innovation and shape the future of manufacturing sustainably and competitively.
Future chapters will explore strategies for industrial 5G actors, various business models, deployment strategies, and benchmarks from use cases in other countries.
About the Author
Abdelhak FODIL is an expert in connectivity and digital transformation with nearly 20 years of experience, specializing in 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT). Currently serving as Head of Department at the French National Frequency Agency (ANFR), he represents France in international meetings to support the deployment of new wireless technologies. He played a key role in preparations for the Paris 2024 Olympic Games, collaborating with major players such as Nokia, Airbus, and SNCF.
Previously at Orange, he led mobile coverage projects for major Parisian events and designed B2B connectivity solutions for industrial and healthcare clients. He also held leadership roles in the deployment of 4G in the northeast regions for Orange and at ATM Mobilis, where he was responsible for radio optimization across a vast region in Algeria, managing 2,000 radio sites. His career began at Alcatel-Lucent, where he oversaw the implementation of radio networks for operator clients.
Academically, Abdelhak FODIL holds a Master’s degree in Mobility, Networks, and Transport from the Université Polytechnique Hauts-de-France and an engineering degree in telecommunications from S-D University. He also recently earned an MBA from the Sorbonne Business School, where he conducted research on the monetization of 5G and its adoption by vertical sectors and industry.



Leave a comment